In China Ecological Civilization newsletter on Substack, Sep 12, 2024, Ying Xue writes:
On the afternoon of September 12, during the inspection of Shaanxi and Gansu, Chinese President Xi Jinping presided over a symposium in Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, on comprehensively promoting ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
In October 2021, China issued the “Outline for Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development in the Yellow River Basin”. Reviewing this document, we can see why Xi attaches so much importance to ecological protection in the Yellow River Basin.
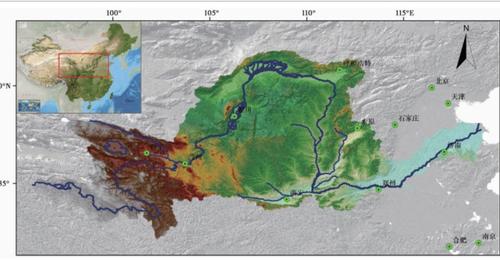
The Yellow River is the second longest river in China and the mother river of the Chinese nation and civilization. The Yellow River Basin is an important ecological security barrier and also an important area for population activities and economic development.
The main stream and tributaries of the Yellow River flow through nine provinces and autonomous regions including Qinghai, Sichuan, Gansu, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Henan, and Shandong, covering an area of about 1.3 million square kilometers. At the end of 2019, the total population was about 160 million. The Yellow River Basin is a major production area for agricultural products, and the output of grain and meat accounts for about one-third of the country’s total.
At the same time, the Yellow River is also one of the rivers with the highest sediment content, and serious flood disasters in the world.
The biggest problem in the Yellow River Basin is the shortage of water resources. Most areas in the upper and middle reaches are located to the west of the 400-millimeter isohyet. The climate is arid and rainless. The multi-year average precipitation is 446 millimeters, only 40% of that in the Yangtze River Basin. The multi-year average total water resources volume is 64.7 billion cubic meters, less than 7% of that of the Yangtze River. The utilization rate of water resources development is as high as 80%, far exceeding the ecological warning line of 40%.
Another serious problem in the Yellow River Basin is ecological fragility. The ecologically fragile areas in the Yellow River Basin are widely distributed and of many types. The plateau glaciers, grasslands and meadows in the upper reaches, as well as the Three-River Headwaters region and Qilian Mountains, the Loess Plateau in the middle reaches, and the Yellow River Delta in the lower reaches are all extremely prone to degradation. The restoration is extremely difficult and the process is slow.
Old problems such as sediment deposition in the lower reaches, river channel swaying, and “suspended rivers on land” have not been completely resolved. Nearly one million people in the lower reaches floodplain areas are still threatened by floods. The risk of extreme floods caused by climate change and extreme weather still exists.
The Yellow River Basin suffers insufficient high-quality development. The industries in the provinces and autonomous regions along the Yellow River rely heavily on energy and are of low quality and low efficiency. There is a lack of emerging industrial clusters with strong competitiveness. The income level of urban and rural residents is lower than the national average.
Since 2012, Xi has defined the water control concept of “giving priority to water conservation, ensuring a balanced spatial distribution of water resources, taking a systematic approach to governance, and relying on both government initiatives and market forces”, and has achieved some results.
At the symposium on September 12, he emphasized that it is necessary to continuously improve the pattern of comprehensive ecological protection and cooperation in the Yellow River Basin and build a national ecological security barrier. Some of the methods he mentioned include:
- Give more prominence to the systematization, integrity, and coordination of Yellow River governance, promote the establishment of an ecological environment governance system that integrates upstream and downstream, deeply implement major projects for the protection and restoration of important ecosystems, and enhance the stability of the basin’s ecosystem.
- Strengthen the joint prevention and control of the “Three-North” project and enhance the overall effect.
- Strengthen the comprehensive treatment of coal mining subsidence areas and actively explore new paths for the transformation and development of resource-based regions.
- Continuously and intensively fight the battle against pollution, strengthen the treatment of important tributaries and key lakes and reservoirs, and improve the construction of environmental infrastructure in areas along rivers and lakes.
- Strengthen comprehensive treatment of air pollution, accelerate the ultra-low emission transformation of key industries, and vigorously promote the clean and efficient utilization of coal. — Implement fiscal, taxation, financial, investment, price policies and standard systems that support green and low-carbon development.
- Improve the mechanism for realizing the value of ecological products.
- Explore the establishment of a basin-wide, market-oriented, and diversified ecological protection compensation mechanism.
- Implementation of the strictest water resources protection and utilization system, improve the level of water resources conservation and intensive utilization, and improve the disaster prevention and mitigation system. Improve the water and sediment regulation mechanism and improve the regulation system mainly composed of major water conservancy projects such as backbone reservoirs.
- Promote an all-round green transformation of the development mode and build a modern industrial system with characteristic advantages.
- Unremittingly focus on the production of grain and important agricultural products, and strengthen the support of agricultural science and technology and equipment.
- Vigorously develop a green and low-carbon economy, orderly promote the planning and construction of large-scale wind power, photovoltaic bases and power transmission channels, and accelerate the replacement of clean energy in key industries.
Meanwhile, Xi also emphasized to strengthen the overall and systematic protection of cultural and natural heritages and further promote archaeological and other work. ###
Watch video about Xi’s speech: https://youtu.be/-8OhKV3g3Co
Source: China Ecological Civilization, Sep 12, 2024. https://xueyingyingxue.substack.com/…/why-did-xi-hold…