
A research team led by scientists from China’s Xi’an University of Technology has assessed the ecological and environmental effects of large-scale PV development in desert areas. The research found that big solar power plants have a positive impact on the ecological environment of desert areas. The study was conducted at a 1 GW solar park in Qinghai province in northeastern China, and reported in the scientific journal Nature.
The results were presented in “Assessment of the ecological and environmental effects of large-scale photovoltaic development in desert areas,” published in scientific reports. The research team included scientists from the State Power Investment Group Qinghai Photovoltaic Industry Innovation Center.
Abstract
Photovoltaic development has played a crucial role in mitigating the energy crisis and addressing global climate change. However, it has also had significant impacts on the ecological environment. To ensure the sustainable growth of the photovoltaic industry, it is essential to establish an indicator system to assess the ecological and environmental effects of photovoltaic development. This study utilizes the Driving-Pressure–Status–Impact-Response (DPSIR) framework to create an indicator system for evaluating the ecological and environmental effects of desert photovoltaic development. The study evaluates the ecological and environmental effects at the on-site (WPS), transitional zone (TPS), and off-site (OPS) areas of the Qinghai Gonghe Photovoltaic Park in China. The entropy weight method was utilized to calculate indicator weights, while the evaluation model and indicators were transformed uniformly to obtain standardized scores for ecological and environmental effects. and conducting a thorough analysis of the distribution characteristics and factors influencing the evaluation indicators’ scores. Overall, the large-scale development of desert photovoltaics in Gonghe County has had a positive impact on the ecological environment. The WPS had better ecological and environmental conditions than did the TPS and OPS, and the ecological and environmental evaluation levels of the WPS were categorized as “general” (0.439), while the ecological and environmental effect evaluation levels of the TPS (0.286) and OPS (0.28) were both “poor”, indicating significant room for improvement. Moreover, all indicators in the scheme layer, which are used to evaluate ecological and environmental quality, yielded higher scores for the WPS than for the TPS and OPS, demonstrating that photovoltaic development has a positive effect on desert area ecology and the environment.
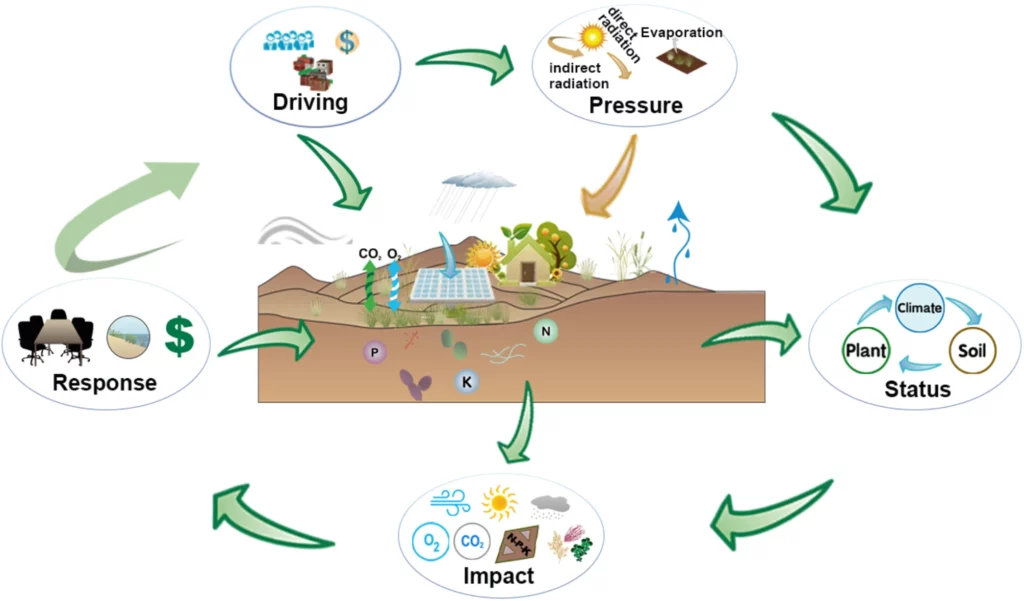
The logical relationships within the Driving-Force-Pressure-Status-Impact-Response (DPSIR) model. In this model, the driving force (D) associated with human activities results in fluctuations in ecosystem pressure (P), which in turn alters the state of the ecosystem (S) and subsequently impacts the ecosystem (I). This dynamic also prompts governmental or societal responses (R) to address the driving forces.
Sources:
Nature, Sept 28, 2024. ‘Assessment of the ecological and environmental effects of large-scale photovoltaic development in desert areas.’ https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-72860-8
PV Magazine, October 10, 2024. https://www.pv-magazine.com/…/large-scale-pv-has…/